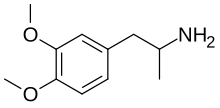
3,4-Dimethoxyamphetamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 3,4-DMA; Dimethoxyamphetamine; DMA; 3,4-Dimethoxy-α-methylphenethylamine; α-Methylhomoveratrylamine; EA-1316; NSC-144717 |
| Drug class | Serotonergic psychedelic; Hallucinogen |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.985 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 195.262 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
3,4-Dimethoxyamphetamine (3,4-DMA), or simply dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA), is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families.[1][2] It is one of the dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) series of positional isomers.[1][2]
The drug has been assessed in various biochemical and preclinical studies.[2] It has been tried in humans at doses of up to 700 mg intravenously, with mescaline-like effects reported.[2][1] 3,4-DMA is also orally active and has produced sympathomimetic effects at a dose of 160 mg.[2][1] Its duration of action is unknown.[2][1]
Its affinity (Ki) for the rat serotonin 5-HT2A receptor has been assessed[2] and was found to be 43,300 nM.[3] For comparison, the affinity of para-methoxyamphetamine (PMA) was 33,600 nM, of 2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine (2,5-DMA) was 5,200 nM, and of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM) was 100 nM in the same study.[3] 3,4-DMA has been found to be a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), with an IC50Tooltip half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 20,000 nM for monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), whereas it was inactive at monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) (IC50 > 100,000 nM).[4][5]
3,4-DMA produces 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyamphetamine (MHA) as its major metabolite in dogs and monkeys.[2]
See also
- 3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA)
- 3,4-Ethylenedioxyamphetamine (EDMA)
- 3-Methoxyamphetamine (3-MA)
- 4-Methoxyamphetamine (PMA)
- 3,4,5-Trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA)
- 3,4-Dihydroxyamphetamine (DHA; α-methyldopamine)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Shulgin AT, Shulgin A (1991). "#55 3,4-DMA; 3,4-DIMETHOXYAMPHETAMINE". PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. ISBN 9780963009609. OCLC 25627628.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Shulgin A, Manning T, Daley PF (2011). "#38. DMA". The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. Vol. 1. Berkeley: Transform Press. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0.
- 1 2 Shannon M, Battaglia G, Glennon RA, Titeler M (June 1984). "5-HT1 and 5-HT2 binding properties of derivatives of the hallucinogen 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane (2,5-DMA)". Eur J Pharmacol. 102 (1): 23–29. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(84)90333-9. PMID 6479216.
- ↑ Reyes-Parada M, Iturriaga-Vasquez P, Cassels BK (2019). "Amphetamine Derivatives as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors". Front Pharmacol. 10: 1590. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01590. PMC 6989591. PMID 32038257.
- ↑ Gallardo-Godoy A, Fierro A, McLean TH, Castillo M, Cassels BK, Reyes-Parada M, Nichols DE (April 2005). "Sulfur-substituted alpha-alkyl phenethylamines as selective and reversible MAO-A inhibitors: biological activities, CoMFA analysis, and active site modeling". J Med Chem. 48 (7): 2407–2419. doi:10.1021/jm0493109. PMID 15801832.
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-specific |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenethylamines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine) |
| ||||||||||
| Tryptamines (serotonin, melatonin) |
| ||||||||||
| Histamine |
| ||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Melatonergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Monoamine releasing agents • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|