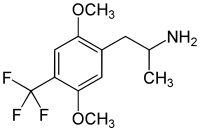
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine; DOTFM |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16F3NO2 |
| Molar mass | 263.260 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine (DOTFM) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and DOx. It was first synthesized in 1994 by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols.[1] DOTFM is the α-methylated analogue of 2C-TFM.
It acts as an agonist at the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors.[1] In drug discrimination tests in rats, DOTFM fully substituted for LSD and was slightly more potent than DOI.[1] In addition, (R)-DOTFM robustly induces the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, in rodents, with equivalent potency as (R)-DOI.[2] The drug is around twice as potent as 2C-TFM in animal studies.
In contrast to (R)-DOI, which has extraordinarily potent serotonin 5-HT2A receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effects,[3][4] DOTFM shows no anti-inflammatory effects.[5] The differences between the drugs in this regard appear to be due to differences in functional selectivity at the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[5][2]
See also
- 2C-iBu (ELE-02)
- Anti-inflammatory § Serotonergic psychedelics
References
- 1 2 3 Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Huang X, Roth BL, Gudelsky GA, et al. (December 1994). "1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-aminopropane: a potent serotonin 5-HT2A/2C agonist". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (25): 4346–4351. doi:10.1021/jm00051a011. PMID 7996545.
- 1 2 Flanagan TW, Foster TP, Galbato TE, Lum PY, Louie B, Song G, et al. (February 2024). "Serotonin-2 Receptor Agonists Produce Anti-inflammatory Effects through Functionally Selective Mechanisms That Involve the Suppression of Disease-Induced Arginase 1 Expression". ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science. 7 (2): 478–492. doi:10.1021/acsptsci.3c00297. PMC 10863441. PMID 38357283.
The effects of (R)-DOTFM were examined in the head-twitch response (HTR) assay. (R)-DOTFM produced a strong HTR with a potent ED 50 of 0.60 μmol/kg. These values are equivalent to (R)-DOI, as previously determined.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - ↑ Nichols DE, Johnson MW, Nichols CD (February 2017). "Psychedelics as Medicines: An Emerging New Paradigm". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 101 (2): 209–219. doi:10.1002/cpt.557. PMID 28019026.
- ↑ Yu B, Becnel J, Zerfaoui M, Rohatgi R, Boulares AH, Nichols CD (November 2008). "Serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor activation suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced inflammation with extraordinary potency". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 327 (2): 316–323. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.143461. PMID 18708586.
- 1 2 Flanagan TW, Billac G, Nichols CD (2022). "Differential Regulation of Inflammatory Responses Following 5-HT 2 Receptor Activation in Pulmonary Tissues". The FASEB Journal. 36 (S1). doi:10.1096/fasebj.2022.36.S1.R2617. ISSN 0892-6638.
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|