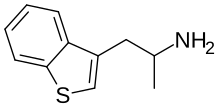
3-APBT
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SKF-6678; SK&F-6678; 3-(2-Aminopropyl)benzo[β]thiophene; α-Methylbenzo[b]thiophene-3-ethylamine |
| Drug class | Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent; Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist; Entactogen; Serotonergic psychedelic |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13NS |
| Molar mass | 191.29 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
3-APBT (former developmental code name SKF-6678), also known as 3-(2-aminopropyl)benzo[β]thiophene, is a monoamine releasing agent and serotonin receptor agonist of the benzothiophene group.[1][2] It is an analogue of α-methyltryptamine (AMT) in which the indole ring has been replaced with a benzothiophene ring.[1][2]
The drug acts as a potent and well-balanced serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA).[2] It is also a full agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors.[2] 3-APBT produces the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, in rodents.[2] It does not stimulate locomotor activity in rodents, suggesting that it does not possess stimulant-type effects.[2] The drug has been reported be a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), specifically of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) (IC50Tooltip half-maximal inhibitory concentration = 16,200 nM).[2][3]
3-APBT was developed by Smith, Kline & French (SKF) as a potential pharmaceutical drug in the late 1950s.[1][4] The drug and its positional isomer 2-APBT were reported to produce various central nervous system (CNS) effects and to be useful as a "ataractics, psychic energizers, and analgetics".[1][4] 3-APBT has also been reported to have appetite suppressant effects in rodents, but to have considerably lower potency than AMT as an "analeptic" in rodents.[1][5]
See also
- 3-APB
- α-Methylisotryptamine (isoAMT)
- 1ZP2MA (indolizine analogue of AMT)
- 1Z2MAP1O (indolizine analogue of BK-NM-AMT)
- C-DMT
- 2-APBT
- 5-APBT
- 6-APBT
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Brandt SD, Carlino L, Kavanagh PV, Westphal F, Dreiseitel W, Dowling G, et al. (August 2020). "Syntheses and analytical characterizations of novel (2-aminopropyl)benzo[b]thiophene (APBT) based stimulants". Drug Testing and Analysis. 12 (8): 1109–1125. doi:10.1002/dta.2813. PMID 32372465.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Rudin D, McCorvy JD, Glatfelter GC, Luethi D, Szöllősi D, Ljubišić T, et al. (March 2022). "(2-Aminopropyl)benzo[β]thiophenes (APBTs) are novel monoamine transporter ligands that lack stimulant effects but display psychedelic-like activity in mice". Neuropsychopharmacology. 47 (4): 914–923. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01221-0. PMC 8882185. PMID 34750565.
- ↑ Vallejos G, Fierro A, Rezende MC, Sepúlveda-Boza S, Reyes-Parada M (July 2005). "Heteroarylisopropylamines as MAO inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (14): 4450–4457. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.04.045. PMID 15908219.
- 1 2 GB 855115A, "Improvements in or relating to β-aminoalkylthianaphthene and β-aminoalkylbenzofuran derivatives", assigned to Smith Kline and French Laboratories Ltd.
- ↑ Campaigne E, Neiss ES, Pfeiffer CC, Beck RA (September 1968). "Benzo[b]thiophen derivatives. XII. Synthesis of some 3-benzo[b]thienylalkylamines and comparison of their central nervous system activity with tryptamine isosteres". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 11 (5): 1049–1054. doi:10.1021/jm00311a031. PMID 5697069.
External links
| Phenylalkyl- amines (other than cathinones) |
|
|---|---|
| Cyclized phenyl- alkylamines | |
| Cathinones |
|
| Tryptamines | |
| Chemical classes | |
| DRAsTooltip Dopamine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAsTooltip Norepinephrine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| SRAsTooltip Serotonin releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-specific |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenethylamines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine) |
| ||||||||||
| Tryptamines (serotonin, melatonin) |
| ||||||||||
| Histamine |
| ||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Melatonergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Monoamine releasing agents • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||