BW-501C67
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | BW-501; BW-501C; α-Anilino-N-2-(3-chlorophenoxy)-propylacetamidine |
| Drug class | Peripherally selective serotonin receptor antagonist |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
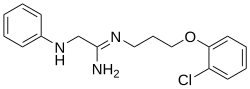
| Formula | C17H20ClN3O |
| Molar mass | 317.82 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
BW-501C67 is a peripherally selective serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor antagonist which is used in scientific research.[1][2][3][4][5][6] It shows selectivity for the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors over the α1-adrenergic receptor.[1]
The drug antagonizes peripheral but not central effects of serotonin receptor agonists like serotonin.[2][3][7][6] As examples, it has been found to antagonize the sympathomimetic effects of serotonin in animals, including vasoconstriction and pressor effects, but does not block centrally mediated effects like increased corticosterone secretion or myoclonus.[3][7][8][6]
BW-501C67 and analogues were patented for use in combination with serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonists like serotonergic psychedelics in 2023.[9]
See also
References
- 1 2 Middlemiss DN, Hibert M, Fozard JR (1986). "Chapter 5. Drugs Acting at Central 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors". Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 21. Elsevier. pp. 41–50. doi:10.1016/s0065-7743(08)61115-x. ISBN 978-0-12-040521-3.
- 1 2 Sharp T, Boothman L, Raley J, Quérée P (December 2007). "Important messages in the 'post': recent discoveries in 5-HT neurone feedback control". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 28 (12): 629–636. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2007.10.009. PMID 17996955.
- 1 2 3 Green AR (December 1984). "5-HT-mediated behavior. Animal studies". Neuropharmacology. 23 (12B): 1521–1528. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(84)90096-0. PMID 6152026.
- ↑ Ramage AG (November 2001). "Central cardiovascular regulation and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors". Brain Research Bulletin. 56 (5): 425–439. doi:10.1016/s0361-9230(01)00612-8. PMID 11750788.
- ↑ Chaouloff F, Layeillon C, Baudrie V (January 1993). "5-HT1C/5-HT2 receptor blockade prevents 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)2-aminopropane-, but not stress-induced increases in brain tryptophan". European Journal of Pharmacology. 231 (1): 77–82. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(93)90686-c. PMID 8095238.
- 1 2 3 Fuller RW, Kurz KD, Mason NR, Cohen ML (June 1986). "Antagonism of a peripheral vascular but not an apparently central serotonergic response by xylamidine and BW 501C67". European Journal of Pharmacology. 125 (1): 71–77. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(86)90084-1. PMID 3732393.
- 1 2 Cook DA (1984). "The pharmacology of cerebral vasospasm". Pharmacology. 29 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1159/000137986. PMID 6379682.
- ↑ Fuller RW (1996). "Serotonin receptors involved in regulation of pituitary-adrenocortical function in rats". Behavioural Brain Research. 73 (1–2): 215–219. doi:10.1016/0166-4328(96)00099-x. PMID 8788505.
- ↑ WO 2023028086, Kruegel AC, "Combinations of peripheral 5-HT2A receptor antagonists and central 5-HT2A receptor agonists", published 2 March 2023, assigned to Gilgamesh Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.