Bufenadrine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | B.S. 6534; BS-6534; 2-tert-Butyldiphenhydramine |
| Drug class | Antiemetic; Antihistamine; Anticholinergic; Antiparkinsonian agent |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
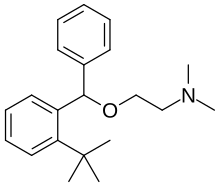
| Formula | C21H29NO |
| Molar mass | 311.469 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Bufenadrine (INN; developmental code name B.S. 6534), also known as 2-tert-butyldiphenhydramine, is a drug described as an antiemetic, antihistamine, anticholinergic, and antiparkinsonian agent which was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] It is the 2-tert-butyl analogue of diphenhydramine.[2] The drug was found to produce stereoselective hepatotoxicity in animals and this led to the discontinuation of its development.[2][5] Bufenadrine was first described in the literature by 1967.[1][4] Its INN suffix "-drine" is generally for sympathomimetics but bufenadrine itself is not actually a sympathomimetic or related agent.[6]
References
- 1 2 Elks J (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer US. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. Retrieved 17 October 2024.
- 1 2 3 Eichelbaum MF, Testa B, Somogyi A (2012). Stereochemical Aspects of Drug Action and Disposition. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 422. ISBN 978-3-642-55842-9. Retrieved 17 October 2024.
- ↑ Ariëns EJ (2013). Drug Design: Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 6. Academic Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-1-4832-1608-9. Retrieved 17 October 2024.
- 1 2 Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Volumes 1-4. William Andrew Publishing. 2013. pp. 704–705. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. Retrieved 17 October 2024.
- ↑ Hespe W, Mulder D, van Eeken CJ (1972). "Differences in metabolic behavior and liver toxicity between the optical isomers of bufenadrine hydrochloride, a substituted diphenhydramine, in the rat". Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 31 (5): 369–379. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1972.tb03600.x. PMID 4678820.
- ↑ "-drine sympathomimetics" (PDF). The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances 2018 (Stem Book 2018). World Health Organization.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.