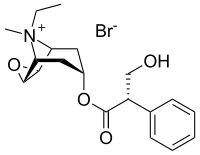
Oxitropium bromide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxivent, Tersigan, Tersigat, Ventilat |
| Other names | N-Ethylscopolammonium bromide; Ba 253; Ba 253BR-L; Ba 253Br; Hyoscine ethobromide; N-Ethylnorscopolamine methyl bromide; Scopolamine ethobromide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.543 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26BrNO4 |
| Molar mass | 412.324 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Oxitropium bromide (trade names Oxivent, Tersigan) is an anticholinergic used as a bronchodilator for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[1]
It was patented in 1966 and approved for medical use in 1983.[2]
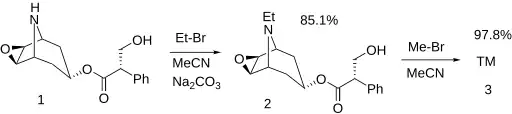
Synthesis
The natural product, norscopolamine (1),[3] is converted by two alkylation reactions into oxitropium bromide. The first, with bromoethane, gives the N-ethyl intermediate (2), which is treated with bromomethane.[4] [5][6]
References
- ↑ Restrepo RD (July 2007). "Use of inhaled anticholinergic agents in obstructive airway disease". Respiratory Care. 52 (7): 833–51. PMID 17594728.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 447. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ↑ Ripperger, H (1995). "(S)-scopolamine and (S)-norscopolamine from Atropanthe sinensis". Planta Med. 61 (3): 292–3. doi:10.1055/s-2006-958082. PMID 7617778.
- ↑ Rolf Banholzer, Werner Schulz, Gerhard Walther, Helmut Wick, Karl Zeile, U.S. patent 3,472,861 (1969 to Boehringer Sohn Ingelheim).
- ↑ Rolf Banholzer, Werner Schulz, & Karl Zeile, U.S. patent 3,538,102 (1970 to CH Boehringer Sohn AG and Co KG, Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH).
- ↑ "Oxitropium bromide". Thieme. Retrieved 2024-07-01.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.