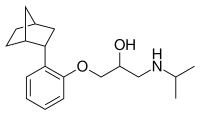
Bornaprolol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[2-(3-Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl)phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C19H29NO2 |
| Molar mass | 303.446 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bornaprolol is a beta-adrenergic antagonist.[1]
Synthesis
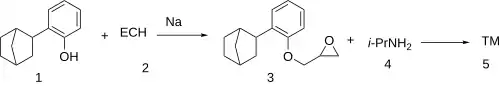
The reaction between 2-(Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl)phenol [17152-43-1] (1) and epichlorohydrin [106-89-8] (2) in the presence of sodium metal gives (3). Opening of the oxirane by treatment with isopropylamine [75-31-0] (4) completed the synthesis of Bornaprolol (5).
References
- ↑ Cheymol, G; Jaillon, P; Lecoq, B; Lecoq, V; Cheymol, A; Krumenacker, M (1987). "Cardiovascular beta-adrenergic blocking effects of bornaprolol in humans: Relation to dose and plasma concentration". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 9 (6): 694–8. doi:10.1097/00005344-198706000-00009. PMID 2442536. S2CID 38782602.
- ↑ Michaud, R.; Bornaprolol hydrochloride. Drugs Fut 1982, 7, 2, 91.
- ↑ Hardy, J.C. et al, Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., Part 2, 1982, 304.
- ↑ DE2735570 idem Jean Mardiguian, U.S. patent 4,157,400 (1985 to Marpha Societe D'etudes Et D'exploitation De Marques S.A., Paris, Fr).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.