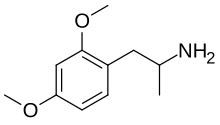
2,4-Dimethoxyamphetamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2,4-DMA; 2,4-Dimethoxy-α-methylphenethylamine; DMA-3 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 195.262 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
2,4-Dimethoxyamphetamine (2,4-DMA), also known as DMA-3, is a drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families.[1][2] It is one of the dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) series of positional isomers.[1][2]
It was reported by Alexander Shulgin to be active at a dose of 60 mg orally and to produce threshold amphetamine-like stimulant and euphoric effects.[1][2] However, there was also a "diffusion of association" and Shulgin stated that it was more than just a stimulant.[1] The duration was described as short and effects subsiding at 3 hours.[1][2] Per Shulgin, the drug could be a full stimulant and/or a full psychedelic at sufficiently high doses, but higher doses were not pursued.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Shulgin AT, Shulgin A (1991). "#53 2,4-DMA; 2,4-DIMETHOXYAMPHETAMINE". PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. ISBN 9780963009609. OCLC 25627628.
- 1 2 3 4 Shulgin A, Manning T, Daley PF (2011). "#35. 2,4-DMA". The Shulgin Index, Volume One: Psychedelic Phenethylamines and Related Compounds. Vol. 1. Berkeley: Transform Press. ISBN 978-0-9630096-3-0.
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.