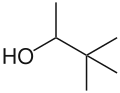
Pinacolyl alcohol
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,3-Dimethylbutan-2-ol | |
| Other names
3,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.681 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C6H14O |
| Molar mass | 102.177 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.8122 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 5.6 °C (42.1 °F; 278.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 120.4 °C (248.7 °F; 393.5 K) |
| 25 g/L | |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Pinacolyl alcohol (also known as 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol and as pine alcohol) is one of the isomeric hexanols and a secondary alcohol.
Pinacolyl alcohol appears on the List of Schedule 2 substances of the Chemical Weapons Convention as a precursor for the nerve agent soman.
See also
- Soman
- Isopropyl alcohol
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–214, 8–106, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
External links
Alcohols | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By consumption |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Primary alcohols (1°) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Secondary alcohols (2°) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Tertiary alcohols (3°) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Hydric alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Amyl alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Aromatic alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Saturated fatty alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Branched and unsaturated fatty alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Sugar alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Terpene alcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Dialcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Trialcohols | |||||||||||||||||
| Sterols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Fluoroalcohols |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Preparations |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Reactions |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Blister agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nerve agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Neurotoxins |
| ||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary/ choking agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Vomiting agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Incapacitating agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Lachrymatory agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Malodorant agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Cornea-clouding agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Biological toxins |
| ||||||||||||||
| Tumor promoting agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.