1-Hexanol
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexan-1-ol[1] | |||
| Other names
amyl carbinol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
|||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
Beilstein Reference |
969167 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.503 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | 1-Hexanol | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2282 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula |
C6H14O | ||
| Molar mass | 102.177 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.82 g cm−3 (at 20 °C)[2] | ||
| Melting point | −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K)[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 157 °C (315 °F; 430 K)[2] | ||
| 5.9 g/L (at 20 °C)[2] | |||
| log P | 1.858 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 100 Pa (at 25.6 °C) | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4178 (at 20 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
243.2 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) |
287.4 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−377.5 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3.98437 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
Pictograms |
 | ||
Signal word |
Warning | ||
Hazard statements |
H302 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
1
2
0 | ||
| Flash point | 59 °C (138 °F; 332 K) | ||
Autoignition temperature |
293 °C (559 °F; 566 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1084 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
1-Hexanol (IUPAC name hexan-1-ol) is an organic alcohol with a six-carbon chain and a condensed structural formula of CH3(CH2)5OH. This colorless liquid is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with diethyl ether and ethanol. Two additional straight chain isomers of 1-hexanol, 2-hexanol and 3-hexanol, exist, both of which differing by the location of the hydroxyl group. Many isomeric alcohols have the formula C6H13OH. It is used in the perfume industry.
Preparation
Hexanol is produced industrially by the oligomerization of ethylene using triethylaluminium followed by oxidation of the alkylaluminium products.[3] An idealized synthesis is shown:
- Al(C2H5)3 + 6C2H4 → Al(C6H13)3
- Al(C6H13)3 + 1+1⁄2O2 + 3H2O → 3HOC6H13 + Al(OH)3
The process generates a range of oligomers that are separated by distillation.
Alternative methods
Another method of preparation entails hydroformylation of 1-pentene followed by hydrogenation of the resulting aldehydes. This method is practiced in industry to produce mixtures of isomeric C6-alcohols, which are precursors to plasticizers.[3]
In principle, 1-hexene could be converted to 1-hexanol by hydroboration (diborane in tetrahydrofuran followed by treatment with hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide):
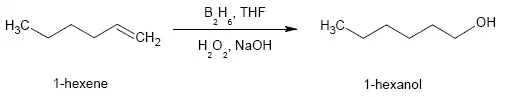

This method is instructive and useful in laboratory synthesis but of no practical relevance because of the commercial availability of inexpensive 1-hexanol from ethylene.
Occurrence in nature
1-Hexanol is believed to be a component of the odour of freshly mown grass. Alarm pheromones emitted by the Koschevnikov gland of honey bees contain 1-hexanol. It also is partly responsible for the fragrance of strawberries.
See also
- Cis-3-Hexenal, another volatile organic compound, is also considered responsible for the freshly mowed grass odor.
References
- ↑ "1-hexanol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 8 October 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- 1 2 Falbe, Jürgen; Bahrmann, Helmut; Lipps, Wolfgang; Mayer, Dieter. "Alcohols, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_279. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2..