Lateral recess
| Lateral recess | |
|---|---|
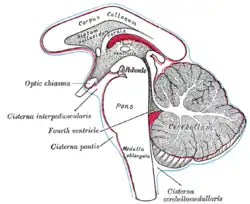 Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisterns. (Lateral recess not labeled, but region is visible.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | recessus lateralis |
| NeuroNames | 642 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.717 |
| TA2 | 5968 |
| FMA | 78470 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
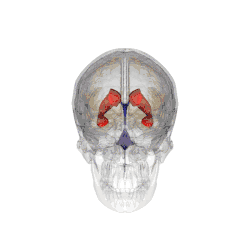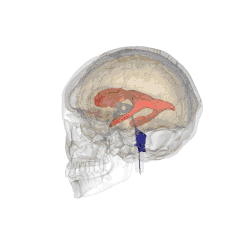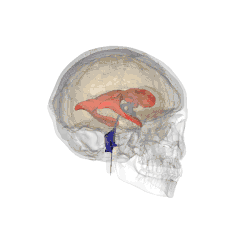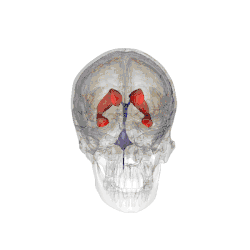
Three-dimensional representation of the ventricular system of the human brain. The fourth ventricle is the lower blue mass. The little points sticking out on the left and right are the two parts of the lateral recess.
The lateral recess or lateral recess of fourth ventricle, is a projection of the fourth ventricle which extends to the lateral border of the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction.[1][2] At this point the fourth ventricle is at its widest.[1]
The lateral recess on each side opens into a lateral aperture (foramen of Luschka) that opens into the subarachnoid space at the cerebellopontine angle. This provides a pathway for the ventricle's cerebrospinal fluid into the subarachnoid space.[1]
In the area of the lateral recess, the vestibular area (containing the vestibular nuclei) and the cochlear nuclei may be found. Nearby, the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle may also be seen.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.