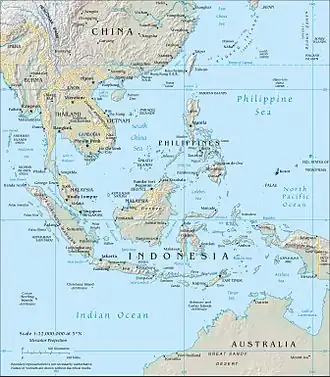
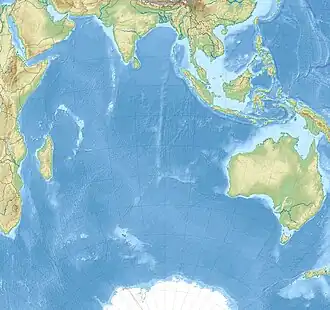
Australasian Mediterranean Sea
| Australasian Mediterranean Sea | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Australasian Mediterranean Sea | |
| Coordinates | 6°30′S 123°54′E / 6.5°S 123.9°E |
| Type | Sea |
| Basin countries | List
|
| Surface area | 9,080,000 km2 (3,510,000 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 7,440 m (24,410 ft) |
The Australasian Mediterranean Sea is a mediterranean sea located in the area between Southeast Asia and Australasia.[1] It connects the Indian and Pacific oceans.[2] It has a maximum depth of 7,440 m[3] and a surface area of 9.08 mil. km².
Geography
.jpg)
.jpg)
In contrast to the American Mediterranean Sea and Mediterranean Sea, it is not surrounded by continents, only by islands and peninsulas. It includes the following seas:
- South China Sea - 3.5 million km2
- Banda Sea - 695,000 km2
- Arafura Sea - 650,000 km2
- Timor Sea - 610,000 km2
- Java Sea - 320,000 km2
- Gulf of Thailand - 320,000 km2
- Gulf of Carpentaria - 300,000 km2
- Celebes Sea - 280,000 km2
- Sulu Sea - 260,000 km2
- Flores Sea - 240,000 km2
- Molucca Sea - 200,000 km2
- Gulf of Tonkin - 126,250 km2
- Halmahera Sea - 95,000 km2
- Bali Sea - 45,000 km2
- Savu Sea - 35,000 km2
- Joseph Bonaparte Gulf - 26,780 km2
- Van Diemen Gulf - 12,035 km2
- Seram Sea - 12,000 km2
- Sibuyan Sea
- Clarence Strait
- Straits of Johor
- Karimata Strait
- Lombok Strait
- Luzon Strait
- Makassar Strait
- Strait of Malacca
- Ombai Strait
- Qiongzhou Strait
- Riau Strait
- Singapore Strait
- Sunda Strait
- Taiwan Strait
- Torres Strait
- Gaspar Strait
- Wetar Strait
States or territories with a coast on the Australasian Mediterranean Sea are: Australia, Brunei, China, Indonesia, Cambodia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, Timor-Leste and Vietnam. It includes the straits of Malacca, Singapore and Luzon, and adjoins the peninsulas of Indochina and Malaysia. The following islands are located within it:
- Bathurst Island, Groote Eylandt, Hainan Dao, Phú Quốc, Ko Chang, Samui archipelago, Nang Yuan, Ko Phangan, Ko Samui, Ko Tao, Tioman, Melville islands, Maluka islands, New Guinea, Paracel Islands, Pratas Island, Philippines, Riau Islands, Sangir Archipelago, Spratly Islands, Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo, Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi), Lesser Sunda Islands (Bali, Flores, Komodo Islands, Lombok, Sumba, Sumbawa, Timor), Taiwan, and Talaud Islands.
See also
- East Indian Archipelago
- Maritime Southeast Asia
References
- ↑ Jochen Kämpf (2010). Advanced Ocean Modelling: Using Open-Source Software. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 138. ISBN 978-3-642-10610-1.
- ↑ International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN). Global Marine and Polar Programme. (1 May 2015). Bridging the gap between ocean acidification impacts and economic valuation: Regional impacts of ocean acidification on fisheries and aquaculture. IUCN. p. 113. ISBN 978-2-8317-1723-4.
- ↑ Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey (2003), Regional Oceanography: an Introduction Archived 2021-05-06 at the Wayback Machine, ch. 13 ("Adjacent seas of the Indian Ocean and the Australasian Mediterranean Sea (the Indonesian throughflow)", pp. 220-8. Daya Publishing House. ISBN 8170353068 (pdf)