Tricarboxylic acid
A tricarboxylic acid is an organic carboxylic acid that contain three carboxyl functional groups (−COOH). A well-known example is citric acid.
Promient examples
| Common name | IUPAC name | Molecular formula | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| citric acid | 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 | 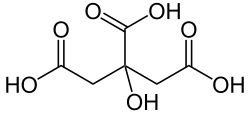 |
| isocitric acid | 1-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H8O7 | 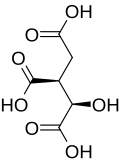 |
| aconitic acid | prop-1-ene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C6H6O6 | 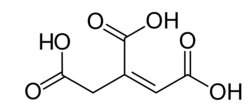 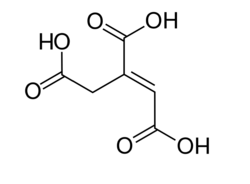
(cis-form and trans-form) |
| propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C3H5(COOH)3 |  |
| agaric acid | 2-hydroxynonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | C22H40O7 | 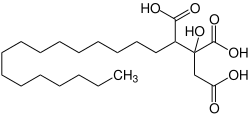 |
| trimesic acid | benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid | C9H6O6[1] | 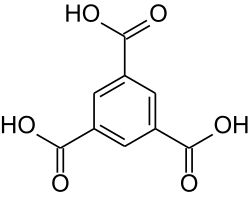 |
Some prominent substituted tricarboxylic acids
Citric acid, is used in the citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or Krebs cycle – which is fundamental to all aerobic organisms.
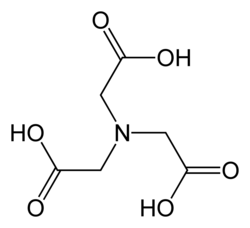
Nitrilotriacetic acid
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is a chelating agent for Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.[2]
See also
- Citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)
- Dicarboxylic acid
- Mellitic acid
References
- ↑ Röhrscheid, Freimund (2000). "Carboxylic Acids, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_249. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4.
- ↑ Schmidt, Thomas; Gousetis, Charalampos; Opgenorth, Hans-Joachim (2022). "Nitrilotriacetic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_377.pub3. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
Literature
- Ryan J. Mailloux, Robin Bériault, Joseph Lemire, Ranji Singh, Daniel R. Chénier, Robert D. Hamel, Vasu D. Appanna (2007). "The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle, an Ancient Metabolic Network with a Novel Twist". PLOS ONE. 2 (8): e690. Bibcode:2007PLoSO...2..690M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000690. PMC 1930152. PMID 17668068.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.