PSR B1509−58
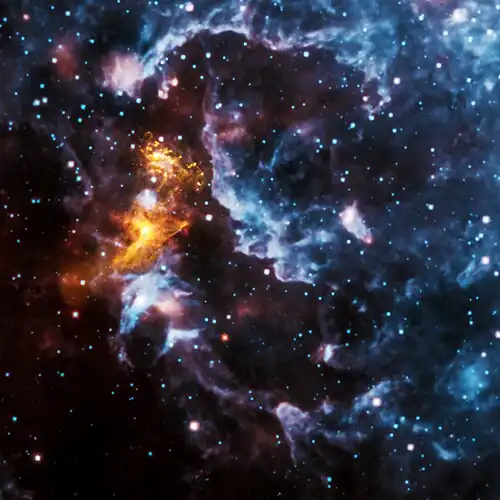 Composite image: X-rays are gold; infrared in red, green and blue/max. Credit: Chandra X-ray Observatory, WISE  | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Circinus |
| Right ascension | 15h 13m 55.52s[1] |
| Declination | −59° 08′ 08.8″[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | Pulsar |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 17,000 ly (5,200 ±1,400 pc) |
| Details | |
| Rotation | 0.1502 s[1] |
| Other designations | |
| PSR 1509-58[1] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
PSR B1509−58 is a pulsar approximately at a distance of 17,000 light-years in the constellation of Circinus discovered by the Einstein X-Ray Observatory in 1982.[2] Its diameter is only 12 miles (19 km). It is located in a Pulsar wind nebula created by itself, that was caused as a remnant of the Supernova (SNR) MSH 15−52 visual approximately 1,700 years ago at the southern celestial hemisphere not visible in the northern hemisphere.[3][4] The nebula spans about 150 light years.[5] The 150 ms pulsations ("almost 7 times per second") are detected in the radio, X-ray, and γ-ray bands.[6]
NASA described the star as "a rapidly spinning neutron star which is spewing energy out into the space around it to create complex and intriguing structures, including one that resembles a large cosmic hand".[7] It is also known by the name "Hand of God".[8] This phenomenon is called pareidolia.

Gallery
- Sequence of images of optical, X-ray, radio, and infra-red emission
- Tour of PSR B1509−58.
- Sequence of PSR B1509−58 images.
- Size comparisons: PSR B1509−58 and Crab Nebula.
 To track this motion, Chandra data is shown, from 2004, 2008, and then a combined image from observations taken in late 2017 and early 2018. These three epochs are shown in the inset of the main graphic.
To track this motion, Chandra data is shown, from 2004, 2008, and then a combined image from observations taken in late 2017 and early 2018. These three epochs are shown in the inset of the main graphic.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Caraveo, P. A.; Mereghetti, S.; Bignami, G. F. (1994). "An Optical Counterpart for PSR 1509-58". The Astrophysical Journal. 423: L125. Bibcode:1994ApJ...423L.125C. doi:10.1086/187252.
- ↑ Seward, F. D.; Harnden, F. R. Jr. (May 1982). "A new, fast X-ray pulsar in the supernova remnant MSH 15-52". The Astrophysical Journal. 256: L45. Bibcode:1982ApJ...256L..45S. doi:10.1086/183793.
- ↑ "How Old Is It?". Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. 2009-04-03. Archived from the original on 2014-01-10. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ↑ Oxford Academic: Modelling spectral evolution of pulsar wind nebulae inside supernova remnants | Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | Oxford Academic, access-date 13. November 2024
- ↑ "PSR B1509-58: A Young Pulsar Shows its Hand". Harvard. 2009-04-03.
- ↑ Romani, Roger W, American Astronomical Society, et al. (1 November 2023). "The Polarized Cosmic Hand: IXPE Observations of PSR B1509-58/MSH 15-52". The Astrophysical Journal. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acfa02.
- ↑ "A Young Pulsar Shows Its Hand". NASA. 7 March 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2024.
- ↑ "NASA photos show giant cosmic hand". CNN. 2009-04-14.
- ↑ Manuel Peitsch. "RCW 89". Manuel's Astrophotography. Retrieved 16 February 2025.
- ↑ Chandra (September 2005). "Chandra Observation of the Interaction between the Hot Plasma Nebula RCW 89 and the Pulsar Jet of PSR B1509-58". The SAO Astrophysics Data System. Retrieved 16 February 2025.
External links
![]() Media related to PSR B1509-58 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to PSR B1509-58 at Wikimedia Commons
- Lee Mohon (24 June 2021). "MSH 15-52: Cosmic Hand Hitting a Wall". NASA. Retrieved 16 February 2025.
- Chandra X-ray Center (CXO): Young Pulsar Shows Its Hand, Science Daily, 5 May 2009, retrieved 15 November 2024
- Chandra X-ray Observatory blog