IZ Aquarii
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius[2] |
| Right ascension | 21h 34m 42.76812s[3] |
| Declination | +01° 49′ 44.9568″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.23 - 6.47[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M4 III[5] |
| B−V color index | 1.398±0.015[2] |
| Variable type | LB[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −20.48±0.26[2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +13.153[3] mas/yr Dec.: −8.518[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.4739±0.2458 mas[3] |
| Distance | 940 ± 70 ly (290 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.75[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.5[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 44.4[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 390.92[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.44[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,303[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.59[6] dex |
| Other designations | |
| IZ Aqr, AAVSO 2129+01, AG+01° 2614, BD+01° 4503, FK5 5868, GC 30209, HD 205358, HIP 106544, SAO 126901, PPM 171943, TYC 542-105-1, GSC 00542-00105, IRAS 21321+0136, 2MASS J21344276+0149447[7] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
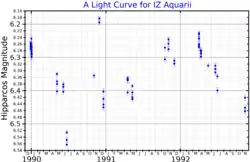
IZ Aquarii is a red giant star in the constellation Aquarius. It is a slow irregular variable that varies between magnitudes 6.23 and 6.47.[4] It can be seen by the naked eye as a very faint star by an observer at an excellent dark-sky location.
The star's variability was first detected in the Hipparcos satellite data, and it was given its variable star designation in 1999.[8]
References
- ↑ "/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Strasbourg astronomical Data Center. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051.
- 1 2 3 Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "IZ Aquarii". The International Variable Star Index. American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- ↑ Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999). "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars, Vol. 5". Michigan Spectral Survey. 05: 0. Bibcode:1999MSS...C05....0H.
- 1 2 3 Khalatyan, A.; Anders, F.; Chiappini, C.; Queiroz, A. B. A.; Nepal, S.; Dal Ponte, M.; Jordi, C.; Guiglion, G.; Valentini, M.; Torralba Elipe, G.; Steinmetz, M.; Pantaleoni-González, M.; Malhotra, S.; Jiménez-Arranz, Ó.; Enke, H.; Casamiquela, L.; Ardèvol, J. (2024). "Transferring spectroscopic stellar labels to 217 million Gaia DR3 XP stars with SHBoost". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 691: A98. arXiv:2407.06963. Bibcode:2024A&A...691A..98K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202451427.
- ↑ "HD 205358". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 20 August 2018.
- ↑ Kazarovets, E. V.; Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; Frolov, M. S.; Antipin, S. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N. (January 1999). "The 74th Special Name-list of Variable Stars" (PDF). Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 4659. Bibcode:1999IBVS.4659....1K. Retrieved 10 October 2024.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.