I have ten observations each from a measurement ($precision$) for two algorithms (let them be called $A$ and $B$) for the same data. I wish to test the alternative hypothesis that the mean precision of $A$ is statistically significantly greater than the mean precision of $B$.
I'm unsure of whether I should use a paired t-test or a Wilcoxon signed-rank test. When I run a Shapiro-Wilk normality test to check for normality, I get p-values > 0.05, indicating that I cannot reject the null hypothesis that they belong to a normally distributed population. However, I cannot conclude they belong to a normally distributed population either.
In light of this uncertainty, I feel that I should go with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test because it makes no assumptions about normality, rather than a t-test which assumes a normal distribution. Is this thinking correct?
Edit: Here are the two qq-plots for $precision$ observations for $A$ and $B$.
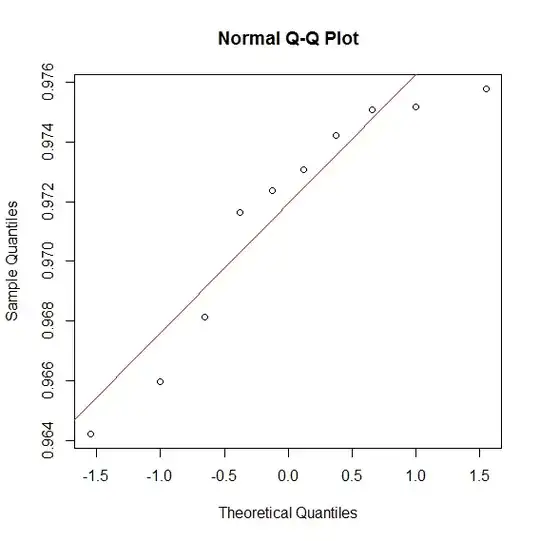

http://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/71953/relative-efficiency-of-wilcoxon-signed-rank-in-small-samples
– Jon Dec 07 '16 at 01:06