Here’s a MILP formulation to partition an Eulerian graph into $K$ Eulerian subgraphs, with an objective of minimizing the maximum cost. Let binary decision variable $x_{ijk}$ indicate whether edge $(i,j)$ appears in subgraph $k$, let $y_{vk}$ be a nonnegative integer decision variable for each node $v$ and subgraph $k$, and let decision variable $z$ represent $\max_k \sum_{i,j} c_{ij}x_{ijk}$. The problem is to minimize $z$ subject to contiguity constraints and
\begin{align}
\sum_k x_{ijk} &= 1 &&\text{for all $(i,j)$} \tag1\label1 \\
\sum_{(i,j):v \in \{i,j\}} x_{ijk} &= 2y_{vk} &&\text{for all $v$ and $k$} \tag2\label2 \\
\sum_{i,j} c_{ij}x_{ijk} &\le z &&\text{for all $k$} \tag3\label3
\end{align}
Constraint \eqref{1} assigns each edge to exactly one subgraph. Constraint \eqref{2} forces every node to have even degree in subgraph $k$. Constraint \eqref{3} enforces the minimax objective.
Here's a flow-based approach to enforce contiguity of subgraph $k$. Let binary decision variable $w_{ik}$ indicate whether node $i$ appears in subgraph $k$. Let binary decision variable $s_{ik}$ indicate whether node $i$ is the source node for subgraph $k$. Let nonnegative variable $f_{ijk}$ be the flow of "commodity" $k$ from node $i$ to node $j$. The following constraints select one source for each $k$ and send one unit of flow from that source to all other nodes in subgraph $k$:
\begin{align}
\sum_i s_{ik} &= 1 &&\text{for all $k$} \\
s_{ik} &\le w_{ik} &&\text{for all $i$ and $k$} \\
w_{ik} \le y_{ik} &\le \frac{\text{degree}_i}{2} w_{ik} &&\text{for all $i$ and $k$} \\
f_{ijk} + f_{jik} &\le n x_{ijk} &&\text{for all $(i,j)$ and $k$} \\
\sum_j (f_{ijk} - f_{jik}) &\le n s_{ik} - w_{ik}
&&\text{for all $i$ and $k$} \\
\end{align}
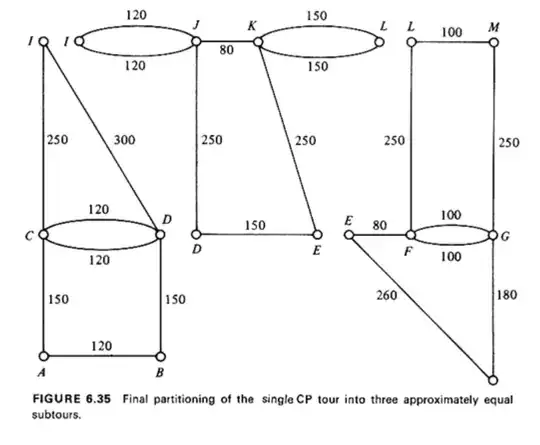
Without the contiguity constraints, the optimal objective value for the example instance with $K=3$ is $1290$, attained by the following subgraphs with weights $1290$, $1270$, and $1240$:
C D 120
C I 250
D I 300
E F 80
E H 260
F G 100
G H 180
A B 120
A C 150
B D 150
C D 120
D E 150
D J 250
E K 250
J K 80
I J 120
I J 120
K L 150
K L 150
F G 100
F L 250
G M 250
L M 100
With the contiguity constraints also imposed, the example solution in the question is optimal, with objective value $1320$.