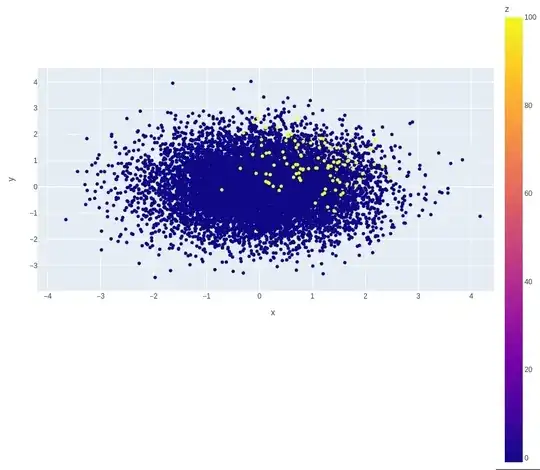
The python script depicted below generates the following toy data set.
I need to determine the values for $x_{min}$, $x_{max}$, $y_{min}$, $y_{max}$ describing a rectangular area where the sum over all $z$s in that area is maximized. In other words: which area is the best compromise between negative values of $z$ and positive $z$ values.
What would be the best approach to achieve this?
Would it make sense to start with the whole area and then make the rectangular box smaller with each iteration? E.g. take away a fraction of the area on the left side, then on the top, the right, and the bottom. Whenever the sum over all $z$s is increased, that step was successful. Once a step does not increase the sum over all $z$s for that box, this step should not be executed but omitted (variant a). Or the fraction with which the area was reduced should be set smaller (variant b).
Would such an approach make sense?
If somebody has an alternative idea: I am glad for any input.
If somebody is even able to supply any coding hints/solutions, such input is very welcome, too.
The code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
np.random.seed(1)
configuration for first array
mean0 = np.array([0., 0.])
cov0 = np.array([[1., 0.], [0., 1.]])
size0 = 10000
configuration for second array
mean1 = np.array([1., 1.])
cov1 = np.array([[.5, 0.], [0., .5]])
size1 = 100
build first array
vals0 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean0, cov0, size0)
append another column to the right of the array
vals0 = np.append(vals0, [[-1] for x in range(size0)], axis=1)
fill new column with randomized data (negative values)
vals0[:, 2] = -1.0 + 0.2 * np.random.random(size0)
build second array
vals1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean1, cov1, size1)
append another column to the right of the array
vals1 = np.append(vals1, [[-1] for x in range(size1)], axis=1)
fill new column with randomized data (positive values)
vals1[:, 2] = 100.0 - 0.2 * np.random.random(size1)
combine first and second array
vals2 = np.append(vals0, vals1, axis=0)
convert numpy array to pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(vals2, columns=['x', 'y', 'z'])
use plotly to visualize the data
fig = px.scatter_matrix(df.sort_values('z'),
dimensions=["x", "y"],
color="z")
do not show diagonal data
fig.update_traces(diagonal_visible=False)
fig.show()