Yes I know it sounds like a superslang portmanteau of modern obscenities (and indeed it is), which is why I was surprised to see it in a 1742 book, and why I'm asking.
Toward the beginning of Book 4, Chapter 5 of The History of the Adventures of Joseph Andrews and of his Friend Mr. Abraham Adams is the following passage, with bolding added by me
"Why, there it is in peaper," answered the justice, showing him a deposition which, in the absence of his clerk, he had writ himself, of which we have with great difficulty procured an authentic copy; and here it follows verbatim et literatim:—
The depusition of James Scout, layer, and Thomas Trotter, yeoman, taken before mee, one of his magesty's justasses of the piece for Zumersetshire.
"These deponants saith, and first Thomas Trotter for himself saith, that on the — of this instant October, being Sabbath-day, betwin the ours of 2 and 4 in the afternoon, he zeed Joseph Andrews and Francis Goodwill walk akross a certane felde belunging to layer Scout, and out of the path which ledes thru the said felde, and there he zede Joseph Andrews with a nife cut one hassel twig, of the value, as he believes, of three half-pence, or thereabouts; and he saith that the said Francis Goodwill was likewise walking on the grass out of the said path in the said felde, and did receive and karry in her hand the said twig, and so was cumfarting, eading, and abatting to the said Joseph therein. And the said James Scout for himself says that he verily believes the said twig to be his own proper twig," &c.
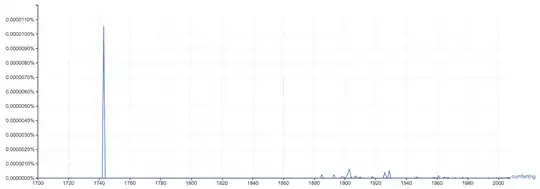
Google Ngram shows virtually no use of the word other than, presumably, copies of this book itself (huge spike in 1742) and, after 1880, mostly few analyses of it.
I found one dissertation by Przemysław Uściński which suggests in a footnote the word cumfarting is part of "a brilliant parody of tedious legal language" (pg. 164).
Helen Thompson suggests something similar, though more specific, in Fictional Matter, her book on chemistry and English novels. In fact she quotes the word specifically and individually (pg. 215):
Typography concretizes—and, in the eyes of the reader whose literacy enlists her in Fielding’s game, rectifies—an abuse of justice also enacted in words.
“Cumfarting” obviously invalidates the juridical text’s claim to propri- ety. In this capacity, language in Joseph Andrews acts: by turning words into things, Fielding lends them qualities that override the prejudicial enactment of the law they would enable.
However everyone seems to be skirting the question: What did cumfarting mean? Or, assuming it's a neologism, what might it have been imagined to mean by an 18th century reader?
Did "cum" and "fart" have the same meanings in 1742 as today (to orgasm & to flatulate, respectively)? Did one but not the other, and it pairing just sounded funny?
Or was it just a completely meaningless pun on "comforting" that only today sounds sexual/filthy? If so, what’s the evidence of meaninglessness? Thompson and Uściński seem to argue it was a double entendre, but don’t specify the second entendre.