Principles: what you can expect from this solution
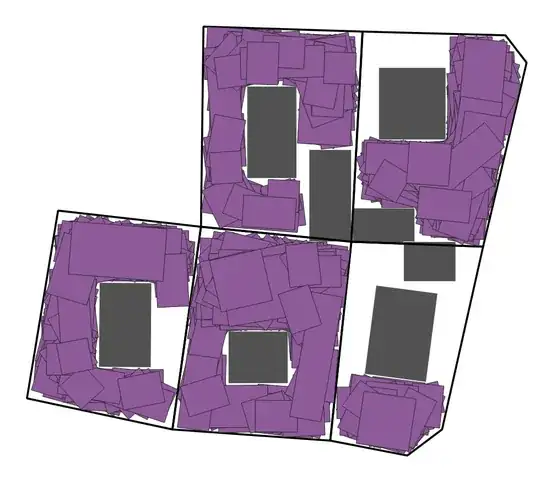
This solution is a heuristic approach. It returns parcels where for sure a 500 sqm rectangle can be placed as well as other "candidate" parcels with a high probability that this will be possible, but that have to be checked manually. See screenshot:
Result: initial building (gray) with buffer (wihte) and remaining parcel (red). The two possible buildings with 500sqm (hatched in gray with black outline). The lower one is completely inside the parcel, thus one that automatically is recognized as a solution; the upper one is not completely, but almost inside the parcel (just 3% of its area outside the parcel) - so a candidate to take into consideration - and indeed, shifting the polygon a bit, it would fall completely inside the parcel:

The solution step by step
Get the parcel that remains when cutting out the buffered buildings (using Difference tool).
Cut narrow connecting "corridors" between the main shapes by buffering with a negative value of lets say -5 m, then apply the inverse, positive value for buffering: 5 m.
Left: building 8gray), buffer (yellow), remaining parcel (red); middle: remaining parcel (red), negative buffer (blue); right: remaining parcel (outlined in red), negative buffer (outlined in blue), the two resulting parcels we will use from now on (solid orange):

Convert from Multipart to single parts and add a unique id (here: fid) to the result.
Use Menu Processing / Toolbox / Minimum bounding geometry and create the Minimum oriented rectangle, based on the fid to get a separate box for each feature.
Scale the polygons from step 4 with a scale factor so that they are the size you want (500 square meters, in your case). The scale factor is the square root of (500 divided by the area of the polygon) (pseudocode).
The parcels from above (orange), the minimum oriented rectangle from step 4 (blue) and these rectangles scaled down to 500 sqm (red) - here using Geometry generator:

The expression 1 (see at the bottom) returns the Minimum oriented rectangle, scaled to an area of 500 sqm, with the same centroid.
Now calculate the intersection of the scaled polygon (step 5) with the parcel polygon from step 3. If the scaled 500 sqm polygon is completely within the parcel, the intersection is the same as the output of step 5. If it is not completely within it, some parts are cut away. Thus now calculate the area of this intersection with the expression 2 from below (an extension of expression 1) creating a new attribute field with Field calculator.
Now select all features where the field calculated in step 6 is near the value of 500 sqm. Ideally, we could just look for the vlaues that are exactly 500 sqm. But we should subtract a ceratain tolerance threshold to account for the fact that sometimes, shifting the scaled polygon inside the parcel could result in a larger interesection. So based on your needs and the type of the data you have, select all values in a certain range (like 450 to 500).
Expressions
Expression 1
with_variable(
'scale',
sqrt (500/$area),
make_rectangle_3points(
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 1), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 1), centroid ($geometry))
),
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))
),
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 3), centroid ($geometry))
)
)
)
Expression 2
area (
intersection (
with_variable(
'scale',
sqrt (5000/area($geometry)),
make_rectangle_3points(
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 1), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 1), centroid ($geometry))
),
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))
),
project (
centroid ($geometry),
@scale*length (make_line (point_n ($geometry, 2), centroid ($geometry))),
azimuth (point_n ($geometry, 3), centroid ($geometry))
)
)
),
overlay_nearest ('parcel',$geometry)[0]
)
)
 .
.