Using the topology you mentioned from the MySQL Documentation
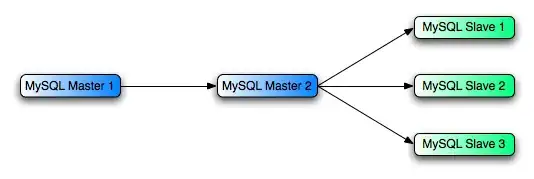
Let's setup the first scenario
EXAMPLE IPs for Each DB Server
Master1 : 10.20.30.40Master2 : 10.20.30.50Slave_1 : 10.20.30.60- replication user is
repluser@'%'
- replication password is
replpass
Make sure binary logging is enabled on all the Slaves
We will do the following
- Promote Master2 to Master1
- Promote Slave_1 to Master2
- Demote Master1 to Slave1
Step 01 : On Master2, run the following
mysql> SET GLOBAL read_only = 1;
mysql> STOP SLAVE;
mysql> RESET SLAVE;
mysql> CHANGE MASTER TO master_host='';
mysql> FLUSH TABLES;
mysql> SET GLOBAL read_only = 0;
Step 02 : Move your CNAME/VIP to Master2
Step 03 : On Slave_1, run mysql> RESET MASTER; FLUSH TABLES;
Step 04 : On Slave_1, dump the data
NEW_MASTER_HOST="10.20.30.60"
MYSQL_USER=root
MYSQL_PASS=rootpassword
MYSQL_CONN="-u${MYSQL_USER} -p${MYSQL_PASS}"
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="--single-transaction"
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} --routines"
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} --triggers"
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} --master-data=1"
MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS="${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} --all-databases"
echo "STOP SLAVE;" > MySQLData.sql
echo "CHANGE MASTER TO master_host='${NEW_MASTER_IP}'," >> MySQLData.sql
echo "master_port=3306," >> MySQLData.sql
echo "master_user='repluser'," >> MySQLData.sql
echo "master_password='replpass'," >> MySQLData.sql
echo "master_log_file='bogus'," >> MySQLData.sql
echo "master_log_pos=1;" >> MySQLData.sql
mysqldump ${MYSQL_CONN} ${MYSQLDUMP_OPTIONS} >> MySQLData.sql
echo "START SLAVE;" >> MySQLData.sql
gzip MySQLData.sql
Step 05 : When Master1 comes back up, rsync or scp MySQLData.sql.gz from Slave_1 to Master1
Step 06 : Login to MySQL on the Master1 and setup it up to replicate from Slave_1
Don't worry about the real binary log filename and position.
Using --master-data=1 embeds CHANGE MASTER TO command with the real coordinates on line 23 of a standard dump.
You can see it with the following
less MySQLData.sql.gz | head -35 | tail -1
Step 07 : Load the data into Master1
MYSQL_USER=root
MYSQL_PASS=rootpassword
MYSQL_CONN="-u${MYSQL_USER} -p${MYSQL_PASS}"
gzip -d < MySQLData.sql.gz | mysql ${MYSQL_CONN}
Step 08 : Login to MySQL on Master1
mysql> SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
and Make sure Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running both say Yes
EPILOGUE
When Done, the topology should be
Master1 : 10.20.30.50Master2 : 10.20.30.60Slave_1 : 10.20.30.40
DISCLAIMER
Please try this out on Test Servers before deploying to Production
GIVE IT A TRY !!!
Note: I would advise that you have multiples slaves
- One for Nightly Backups
- The others for load balancing
SELECTs
