Bmesh script
Script to flatten spheres on their intersection plane. See intersection of two spheres on Paul Bourke's magnificent geometry site The code runs through each selected sphere, checks if they intersect, if they do clalculates the location of the circle of hit.
If there's a collision, for both spheres, selects all vertices that are within the conic angle of the collision and moves them to the point of intersection with the collision disc. NOTE: script relies on the origin of the spheres being the (default) centre of geometry.
 Test run on UV Spheres.
Test run on UV Spheres.
The script
Select all the spheres you want to modify and run script. Alter the scale to change the angle of effect of flattening vertices.
import bpy
import bmesh
from math import acos, degrees, radians
from mathutils import Vector
from mathutils.geometry import intersect_line_plane
context = bpy.context
scene = context.scene
spheres = [(o, max(axis for axis in o.dimensions) / 2) for o in context.selected_objects]
bmeshes = {}
scale = 1.0 # alter to widen bump angle.
def new_bmesh(me):
bm = bmesh.new()
bm.from_mesh(me)
return bm
def squish(sphere, angle, global_plane_co, global_plane_no):
mw = sphere.matrix_world
mwi = mw.inverted()
bm = bmeshes.setdefault(sphere.name, new_bmesh(sphere.data))
local_p = mwi * global_plane_co
local_norm = mwi * (global_plane_co + global_plane_no) - local_p
# select all verts via angle
proj = angle > radians(90)
if proj:
angle = radians(180) - angle
verts = [v for v in bm.verts if v.co.angle(local_p) > angle]
else:
verts = [v for v in bm.verts if v.co.angle(local_p) < angle]
for v in verts:
v.select = True
d = local_norm if proj else v.co
o = v.co if proj else Vector()
hit = intersect_line_plane(o, d, local_p, local_norm)
if hit and hit.length < v.co.length:
v.co = hit
while spheres:
sphere, R = spheres.pop()
P = sphere.matrix_world.translation
for s, r in spheres:
p = s.matrix_world.translation
v = (p - P)
d = v.length
v.normalize()
if d >= r + R:
continue
elif abs(r - R) > d:
continue
elif d < 0.0001:
continue
x = (d * d - r * r + R * R) / (2 * d)
# define plane
pt = P + x * v
norm = v
angle1 = acos(x / R)
angle2 = acos((d - x) / r)
#print(R, r, x, degrees(angle1), degrees(angle2))
squish(sphere, scale * angle1, pt, norm)
squish(s, scale * angle2, pt, norm)
for name, bm in bmeshes.items():
me = scene.objects[name].data
bm.to_mesh(me)
me.update()
scene.update()
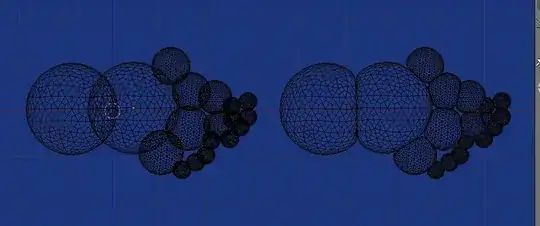 Sample run on icosphere cluster on left, result on right
Sample run on icosphere cluster on left, result on right
EDIT: fix for inside cases, now projects back onto plane if hit is inside (angle is greater than 90 degrees.







