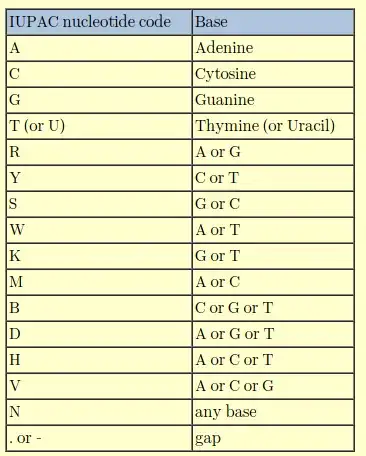
When a DNA sequence is sequenced, I've only ever dealt with A,T,C,G and N which indicates un-identifiable bases. However, I came across a 'k' recently and I had asked another researcher who gave me an answer for what 'k' represents but I don't quite recall. It can't just be an anomaly in that one sequence file. Any ideas?
Asked
Active
Viewed 2,676 times
8
-
K is also the lysine amino acid (and k-mers are something else of course) – Chris_Rands Dec 29 '19 at 21:28
2 Answers
16
4
It is recommended you learn the degenerate nucleotide code. In sequencing it can signify poor quality sequence data, but in primer design it is useful. R (mutation within purines) and Y (mutation within pyrimidines) are common. K, a purine to pyrimadine or pyrimadine to purine mutation is, in my opinion, rare. I would treat a K mutation with caution and consider the triplet codon around it, i.e. if it is part of a protein gene.
Most phylogeneitcs programs will work with the degenerate nucleotide code, so in theory you can still obtain useful information with it.
M__
- 12,263
- 5
- 28
- 47