Ensartinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ensacove |
| Other names | X-396 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.306.918 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
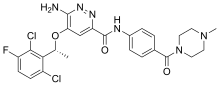
| Formula | C26H27Cl2FN6O3 |
| Molar mass | 561.44 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ensartinib, sold under the brand name Ensacove, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.[1] Ensartinib is an Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor used as the salt ensartinib hydrochloride.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
The most common adverse reactions include rash, musculoskeletal pain, constipation, cough, pruritis, nausea, edema, pyrexia, and fatigue.[2]
Ensartinib was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2024.[1][2][3][4]
Medical uses
Ensartinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer who have not previously received an ALK-inhibitor.[1][2]
History
Efficacy was evaluated in eXALT3 (NCT02767804), an open-label, randomized, active-controlled, multicenter trial in 290 participants with locally advanced or metastatic ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer who had not previously received an ALK-targeted therapy.[2] Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive ensartinib or crizotinib.[2]
Society and culture
Legal status
Ensartinib was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2024.[2][3][5]
Names
Ensartinib is the international nonproprietary name.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Ensacove (ensartinib) capsules, for oral use" (PDF). Xcovery Holdings, Inc. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. December 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "FDA approves ensartinib for ALK-positive locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 18 December 2024. Retrieved 20 December 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 "Novel Drug Approvals for 2024". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 1 October 2024. Retrieved 20 December 2024.
- ↑ New Drug Therapy Approvals 2024 (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). January 2025. Archived from the original on 21 January 2025. Retrieved 21 January 2025.
- ↑ "FDA Approval of Ensartinib for ALK-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)" (Press release). Xcovery Holdings. 19 December 2024. Retrieved 20 December 2024 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2017). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 77". WHO Drug Information. 31 (1). hdl:10665/330984.
External links
- "Ensartinib (Code C102754)". NCI Thesaurus.
- Clinical trial number NCT02767804 for "eXalt3: Study Comparing X-396 (Ensartinib) to Crizotinib in ALK Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients" at ClinicalTrials.gov